Benefits of Stainless Buffing for Metal: More Than Just Shine
Buffing stainless steel is often seen as just about making it look pretty, but there’s more to it than that. The process of smoothing and shining the surface actually offers several important advantages for the metal itself and its performance.
The benefits of buffing stainless steel extend beyond aesthetics and include improving corrosion resistance by creating a smoother surface where corrosive agents are less likely to adhere, making the surface easier to clean and sanitize, reducing friction, and providing a desirable finished appearance for aesthetic or functional purposes. It refines the metal’s surface properties.

A smooth, reflective polished stainless steel surface.
Understanding these benefits highlights why buffing is a crucial process in many industries and applications for stainless steel.
What are the benefits of polishing stainless steel?
Beyond just looking good, what practical advantages does polishing provide for stainless steel?
The benefits of polishing stainless steel include enhanced corrosion resistance due to a smoother surface that resists pitting and the accumulation of contaminants, improved hygiene and ease of cleaning, increased reflectivity for aesthetic appeal or specific applications, and a more consistent and desirable surface finish for various industrial and consumer products.

Where polished stainless steel is commonly used.
Polishing stainless steel involves removing microscopic peaks and valleys on the surface, creating a much smoother profile. This smoothness is where many of the practical benefits come from. On a rough or unpolished surface, tiny imperfections and scratches can act as anchor points where dirt, grime, bacteria, and corrosive substances can collect and adhere. This makes cleaning difficult and can lead to surface corrosion, even on stainless steel which is generally resistant. A smooth, polished surface significantly reduces the number of these anchor points. Contaminants are less likely to stick and can be wiped away much more easily. This is particularly important in industries like food processing, pharmaceuticals, and medical where hygiene and ease of sterilization are paramount. The improved corrosion resistance is a direct result of this smoothness; by reducing the places where corrosive agents can reside, the likelihood of pitting or localized corrosion is reduced. Furthermore, a polished surface can reduce friction, which is beneficial in applications involving moving parts. Of course, the aesthetic appeal is a major benefit, providing a clean, modern, and high-quality look that is desirable in architectural elements, appliances, and consumer goods. Achieving this smooth surface requires careful preparation with quality abrasives like NOVOGRIT discs before the final buffing stages.
What are the advantages of buffing process?
Focusing on the buffing stage itself, what does this final step contribute to the metal?
The advantages of the buffing process, which follows abrasive preparation, include refining the surface to an even higher level of smoothness, achieving specific levels of luster ranging from satin to mirror finish, removing the fine scratch patterns left by the final abrasive steps, and creating a non-porous surface that further enhances corrosion resistance and cleanability.
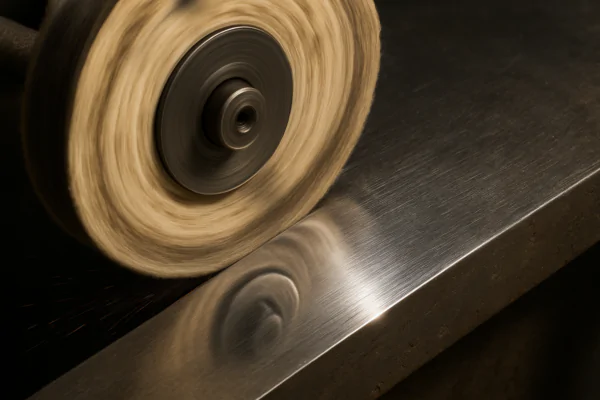

The buffing process actively shining the metal surface.
The buffing process is the final act in achieving a highly refined surface finish on metal. After the surface has been progressively sanded with increasingly finer abrasives to remove imperfections and establish a uniform texture (a process where high-quality abrasives like NOVOGRIT are essential), buffing takes over. This stage uses specialized buffing wheels and compounds containing very fine abrasive particles suspended in a binder. The action of the wheel, combined with the compound, micro-levels the surface even further. It essentially smooths out the microscopic valleys and reduces the peaks, eliminating the fine scratch patterns left by the final sanding grits. The result is a surface that is significantly smoother than what can be achieved with abrasives alone. This extreme smoothness is what creates the high luster or mirror finish. Beyond aesthetics, this micro-leveling reduces the surface area available for contaminants to adhere, further boosting the material’s resistance to corrosion and making it exceptionally easy to clean. Different buffing compounds and wheels allow for control over the final level of shine, from a less reflective bright finish to a true mirror polish. The buffing process is what unlocks the full potential for reflectivity and surface integrity in stainless steel.
Does polishing stainless steel prevent rust?
While stainless steel is known for resisting rust, does polishing it offer additional protection against corrosion?
Yes, polishing stainless steel enhances its resistance to rust and corrosion. While stainless steel’s primary resistance comes from its chromium content forming a passive oxide layer, polishing creates a smoother surface with fewer imperfections. These imperfections on an unpolished surface can trap corrosive agents, leading to localized breakdown of the passive layer and potential pitting or rust formation. A polished surface minimizes these traps.
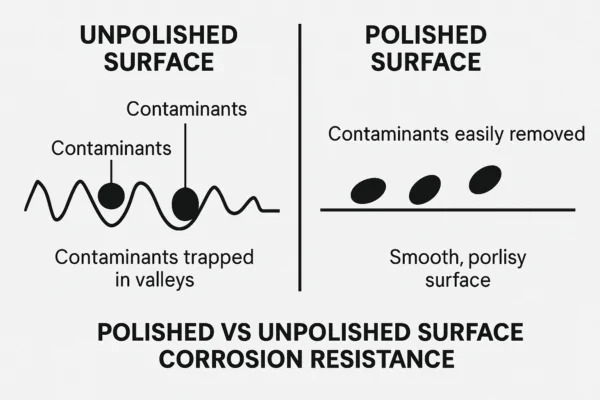
How a smooth, polished surface resists trapped contaminants.
Stainless steel resists rust because of its chromium content (typically at least 10.5%). When chromium is exposed to oxygen, it forms a very thin, invisible passive layer of chromium oxide on the surface. This layer acts as a barrier, protecting the underlying metal from corrosion. If this layer is damaged, it can often reform if oxygen is present. However, surface imperfections, such as those left by machining, grinding, or even relatively coarse sanding, can create microscopic crevices and valleys. These areas are difficult to clean thoroughly and can trap moisture, chlorides (from salts), or other corrosive chemicals. When these agents are trapped, they can locally deplete the oxygen needed for the passive layer to repair itself, or they can aggressively attack the layer, leading to localized breakdown, such as pitting corrosion or crevice corrosion. Polishing, particularly to a high finish, dramatically reduces the number and depth of these surface imperfections. By creating a much smoother surface, it makes it harder for corrosive substances to adhere and collect. It also makes the surface easier to clean, ensuring that potential corrosive agents are removed before they can cause damage. So, while the material itself is "stainless," a polished surface provides an additional layer of protection by maintaining the integrity of that passive layer and preventing the conditions under which localized corrosion is most likely to occur. Effective initial preparation with quality abrasives like those from NOVOGRIT is the necessary foundation for achieving a surface smooth enough for effective polishing and enhanced corrosion resistance.
What does buffing do to metal?
In simple terms, what is happening to the metal’s surface during the buffing process?
Buffing is a process that mechanically smooths and polishes a metal surface using fine abrasive particles applied via a rotating wheel. It removes very small amounts of surface material, leveling microscopic peaks and valleys, which reduces surface roughness, eliminates fine scratches from previous steps, and creates a highly reflective, sometimes mirror-like, finish by bringing out the metal’s inherent luster.
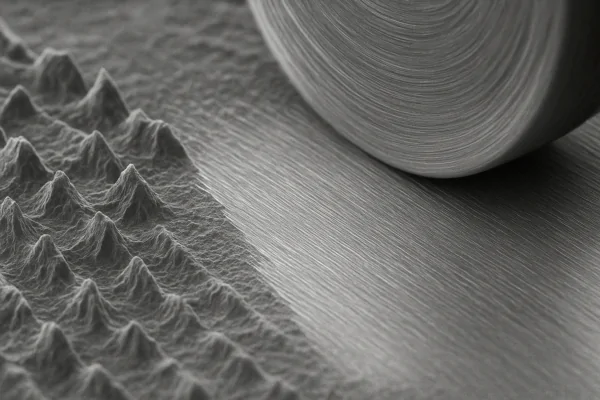
Visualizing the smoothing action of buffing on a metal surface.
Think of buffing as extremely fine-scale abrasion. Unlike sanding, which uses bonded abrasives on paper or cloth to remove material more aggressively and create a desired scratch pattern (or prepare for a finer one), buffing uses loose or semi-bonded fine abrasive particles embedded in a compound applied to a soft wheel. As the wheel spins and contacts the metal surface, these fine particles rub against the metal. They essentially act like tiny cutting or lapping tools, shaving off microscopic amounts of material from the highest points on the surface. This process reduces the difference between the highest peaks and the lowest valleys, making the surface much flatter and smoother at a microscopic level. The result is a surface with significantly reduced roughness. This reduction in roughness is what leads to the visual effect of polishing – light reflects more uniformly off a smooth surface, making it appear shiny. Buffing effectively removes the very fine scratch patterns left by the final abrasive steps, bringing out the natural reflectivity and luster of the metal itself. It’s a process of surface refinement that impacts both the appearance and the functional properties like cleanliness and corrosion resistance.
Conclusion
Buffing stainless steel provides significant benefits beyond just a nice look, including enhanced corrosion resistance, easier cleaning, and reduced friction. It’s a process that refines the metal surface through fine abrasion, improving both its function and appearance.
You may also be interested in:

What is the difference between zirconium, ceramic, and aluminum oxide abrasives?
Choosing the right abrasive can be confusing. Using the wrong one wastes time, ruins your workpiece, and costs you money. Let’s make the choice simple for you. The main difference


Best Sandpaper for Aluminum: NOVOGRIT's Guide to Flawless Finishes
What is the Best Type of Sandpaper to Use on Aluminum? Do you find yourself frustrated by sandpaper that gums up instantly when you try to smooth aluminum? It is

Best Sandpaper for Paint Removal: Grits, Types, & Tips | NOVOGRIT
What is the Best Sandpaper for Removing Paint? Are you tired of staring at chipped, peeling paint on your furniture, walls, or even your car? It's a common problem, and

Automotive Wet Sanding: Supplies, Liquids & Best Sandpaper
Automotive Wet Sanding Supplies: What Do You Really Need? Wet sanding is a crucial technique in automotive refinishing, used to achieve a flawlessly smooth surface before painting or polishing. Unlike

Best Sandpaper for Paint Removal & Grit Guide
What Is the Best Sandpaper for Removing Paint? Removing old paint can be a tedious job, but using the right sandpaper makes all the difference. It's not just about grit;

Hardwood Floor Sanding: Screen vs. Sandpaper & Best Practices
Sanding Screen vs. Sandpaper for Hardwood Floors: Which is Best? When you're tackling hardwood floor projects, choosing the right abrasive is crucial for achieving a smooth, professional finish. Both sanding

Paper Backing vs. Mesh Sanding Discs: Which Abrasive to Choose?
Paper Back vs. Mesh Sanding Discs: Which One Should You Pick? Choosing the right sanding disc backing can significantly impact your project's efficiency and finish quality. Paper-backed discs are a

Sanding Mesh vs Paper: Which is More Economical and Better?
Is Sanding Mesh More Economical Than Sandpaper? Comparing Abrasive Costs When stocking up on abrasives, cost is always a factor. Paper sandpaper has traditionally been the standard, but newer mesh

Sanding Nets & Screens Use Cases: When to Choose Mesh Abrasives
Sanding Nets and Screens: What Are Their Best Use Cases? When you encounter sanding nets or screens, you might wonder where they fit into your sanding projects. Unlike traditional solid-backed
